Deciding to divorce is never easy, and the legal steps involved can feel overwhelming in addition to the emotional considerations. In Singapore, divorce affects approximately 7,000 couples a year, making it a reality for many couples.
What is Divorce?
There are two main types of divorce: contested, and uncontested.
Briefly, a contested divorce is one where parties are unable to agree on a divorce settlement, whilst an uncontested divorce is one where both parties have reached an agreement on all aspects of the divorce.
Requirements for Divorce
To file for a divorce in Singapore:
- Either spouse must be domiciled in Singapore or habitually resident in Singapore for at least 3 years before applying for the divorce.
- Parties must have been married for at least 3 years.
- A spouse may qualify to apply for divorce if he/she has suffered exceptional hardship or exceptionally unreasonable and cruel behaviour.
Generally, Singapore citizens and Permanent Residents who have been married for at least 3 years would qualify. However, other Employment Pass (EP) or Work Pass holders who have been habitually resident in Singapore for at least three years will also qualify.

Preparing for Divorce: Key Settlements Terms to Consider
Before commencing the divorce proceedings, parties are encouraged to discuss and agree on possible settlement terms. The terms should generally cover two main areas: (1) the Grounds for Divorce, and (2) the Ancillary Matters.
Grounds for Divorce
In both contested and uncontested divorce, couples must provide proof of the marriage’s irretrievable breakdown through any of the following legal facts (also referred to as grounds for divorce) under the Women’s Charter:
Unreasonable Behaviour
One spouse has behaved in such a way that the other spouse cannot reasonably be expected to live with them. The Family Justice Courts (“FJC”) adopts a cumulative approach and will look at the overall effect of the respondent’s behaviour on the applicant, not just isolated incidents.
Some common reasons are:
Verbal Abuse or Constant Criticism
Verbal abuse or persistent criticism includes repeated insults, derogatory remarks, or other comments intended to belittle the other party. This could include the respondent calling the spouse “useless” or saying, “marrying you was a mistake.” Over time, a pattern of such behaviour can demonstrate that it is unreasonable to expect the parties to continue living together.
Neglect or Lack of Affection
Neglect or lack of affection occurs when a spouse becomes emotionally distant, avoiding both communication and intimacy. Common scenarios could include the respondent moving to a separate bedroom and refusing all attempts at conversation, making it intolerable for the applicant to continue the marriage.
Controlling Behaviour
Controlling behaviour involves closely monitoring whereabouts, forbidding social contact, or restricting financial freedom. For example, the respondent may refuse the applicant from working or having a personal bank account. Such behaviour undermines the applicant’s well-being and makes cohabitation unbearable, providing grounds for divorce.
Chronic Financial Irresponsibility
Repeated refusal to contribute to household expenses, reckless spending, habitual gambling, or incurring debts that compromise the family’s financial stability may amount to unreasonable behaviour. For instance, the respondent consistently avoids contributing financially and accumulates significant debt through online gambling, causing serious strain on the household and distress to the children, making cohabitation unbearable.
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse refers to habitual drunkenness or drug use that causes distress to the spouse or family. A common scenario may involve the respondent frequently returning home intoxicated and creating disturbances in front of the children. Over time, such behaviour can severely affect the well-being of the family and may be relied upon as a ground for divorce.
Infidelity or Inappropriate Relationships
Infidelity does not always mean physical adultery; emotional affairs or inappropriate conduct can also be cited as grounds for divorce. One scenario is when the respondent maintained an emotional relationship with a colleague despite objections from the other party, which damaged trust and contributed to the breakdown of the marriage.
Violence or Threats
This includes physical abuse, threats of harm, or intimidation. One example is when the respondent threatened to harm the other party during an argument and, in anger, broke a chair. Such behaviour creates an unsafe environment and can make it unreasonable to continue the marriage.
Excessive Work Commitment / Absenteeism
Frequent absence from home due to long working hours, travel, or disengagement can lead to emotional neglect. For example, the couple spent less than an hour together each week due to the respondent’s demanding work schedule. When one partner consistently prioritises their job over family life, it weakens communication and closeness, contributing to the marriage’s breakdown.
Adultery
One spouse has committed adultery, and the other spouse finds it intolerable to live with them.
When a spouse has been caught “cheating”, it means that the spouse is/was having a relationship with a third party, which is “adulterous” from a moral or religious perspective. However, adultery in law means having sexual intercourse with a person who is not one’s spouse.
The challenge for many plaintiffs looking to use this as a ground for divorce is they do not have clear evidence of adultery, unless the spouse readily admits to it. Even with a verbal confession, it can easily be denied later.
It is common for suspicious spouses to use a private investigator to conduct surveillance on the other spouse to gather proof of adultery, as the Court has given judgment for a plaintiff based on strong circumstantial evidence. However, the evidence obtained in the form of video recordings or photographs must be scrutinised property to see if it would be of value in court.
Evidence by way of various forms of communication (such as text messages, emails) or social media posts can also be used as circumstantial evidence to prove adultery.
Desertion
One spouse has deserted the other for a continuous period of at least two years immediately before filing for divorce. Desertion must satisfy four requirements:
- The deserted spouse must not have consented to the separation.
- The deserting spouse must be capable of forming the intention to desert. For example, a wife who, as a result of mental illness, was under the impression that her husband was attempting to murder her and left, is incapable of forming the necessary intention to desert.
- There must be an absence of a reasonable cause for the separation to constitute desertion. The plaintiff (deserted spouse) should show that they have been living separately, and that the defendant (deserting spouse) has the intention to desert. This is usually shown by proving that the defendant spouse has no intention of returning.
- The spouse must form an intention to end the matrimonial union when he/she leaves. This intention need not necessarily be communicated.
Separation with Consent (no-fault divorce)
The plaintiff has to satisfy the requirement that the spouses have lived separately continuously for a period of 3 years. To prove the defendant’s consent to the divorce, the Court also requires the following details:
- Date which the plaintiff and defendant commenced their separation
- Reasons for both parties’ intention to commence separation
- Duration of the separation
- Residential address of each party during the period of separation
- If the parties have been living in separate households under the same roof for the period of the separation (i.e., in different rooms), to give details on how the parties have been living in separate households.
If the plaintiff has the consent of the defendant, the divorce application can proceed on the basis of living separately for three years, provided there are sufficient details to satisfy the Court of what has been explained above.
An amicable and common way to show the Court evidence of the above is through a written deed of separation signed by both spouses.
Separation without Consent
Similar to Separation with Consent, the same 5 requirements must be fulfilled. However, for a Separation without Consent, the minimum period of separation must be 4 years and above.
The plaintiff also does not need to get the defendant spouse’s consent to proceed with the divorce.
Divorce by Mutual Agreement (no-fault divorce)
This is a new fact of Divorce that was introduced on 1 July 2024, where both parties agree that the marriage has irretrievably broken down.
To file for divorce by mutual agreement, the main requirements are:
- The couple must be married for a minimum of 3 years;
- Both spouses agree with reasons for concluding that the marriage has irretrievably broken down;
- That the spouses have made efforts to reconcile;
- The considerations that have been given to post-divorce arrangements for their financial affairs and any children.
If all ancillary issues concerning asset division, custody, care and control, co-parenting arrangements, child maintenance, and spousal maintenance are agreed upon, then the uncontested divorce can proceed on a simplified track.
Read our full article on Divorce by Mutual Agreement to find out more.
Ancillary Matters in Divorce
In a divorce, couples will also have to discuss all ancillary issues for post-divorce arrangements regarding children, spousal maintenance and the division of matrimonial assets. In our experience, couples may be able to agree that they should get a divorce fairly easily, but struggle in coming to an agreement on what is fair when it comes to ancillary matters.
Children
If you are getting divorced and you have children, there are several things that you should take note of.
Children's Care Arrangments - Child Custody, and Care & Control
It is common for individuals to confuse “custody” with “care and control”. This is understandable as custody has a specific legal meaning, and is not used in the ordinary sense of the word or as seen in TV shows.
Custody of a child refers to the authority to exercise parental responsibility in making decisions for the child in major areas such as education, religion, and medical matters. In a joint custody order, it is crystal clear that both parents have parental responsibility over such important matters.
Care and control, and access orders relate largely to the practical day-to-day care and living arrangements for the children. Care and control responsibilities are given to the parent who the child or children of the marriage will live with after the divorce. They will have the day-to-day responsibilities of caring for them, including overseeing the child’s schooling needs, transport arrangements, daily routines, meals, and rest times.
In the case of young children, care and control is traditionally awarded solely to mothers due to the reasoning that it is generally in the welfare of the child to live with their mothers. Fathers who seek sole care and control of their child must be able to show how this would be best for the child, or obtain the mother’s consent. While there are fewer such cases, it is not impossible. You can read our article on Care and Control for Fathers.
Access
Access is the term used in a Court order to allow access of the child to the parent who is not granted care and control. It is described in terms of time spent with the child and is usually worded in terms of reasonable access. This is done purposefully so that the nature of the access order is general and flexible, allowing parents to work out what is best for the children and most practical.
This is especially so when the access order is made while the child is in preschool and will eventually go to primary school, where routines will change.
We have observed cases where a parent may wish to set out a timetable to secure a fixed amount of time with the child during the access period. This could include having access during special occasions after the divorce, such as birthdays, Chinese New Year reunion dinners, public holidays, school holidays, and religious occasions. For some parents, they may also wish to have an access order that allows them to have the child accompany them for an overseas trip to the parent’s home country. These access terms must be agreed upon by both parties—otherwise, they will be contested and have to be heard by a district judge at the ancillary matters hearing.
In certain circumstances, the Courts may also grant supervised access orders to protect the child from potential physical or emotional abuse. Such orders may be made to assess the relationship between the child and the parent who was not granted custody. In cases where the parent may not have a close relationship with the child or needs counselling support to improve their relationship, the Court may also order supervised access if it would protect the child and facilitate the improvement of the relationship.
Children's Maintenance
When speaking of financial support for a child or spouse, the term “alimony” is often used, but this is a term used in the USA. In Singapore and most Commonwealth countries, the correct term is child or spousal maintenance.
Typically, a child’s maintenance is to be paid until the child turns 21 and is usually paid on a monthly basis. The disputes that often arise are the share each parent should pay, what the maintenance should cover, and what is a reasonable amount. The law defines a child as a child of marriage under the age of 21—meaning any order for custody or maintenance will automatically cease to apply after the child reaches that age.
However, there are exceptions where the Court has ordered maintenance extending beyond the age of 21. This is not uncommon where the child is male and serves National Service for 2 years, and then continues with tertiary university studies.
The Court also has the power to grant maintenance if there is proof that a parent has neglected or refused to provide reasonable maintenance for the child who is unable to maintain himself or herself, and order that parent to pay a monthly allowance or a lump sum for the maintenance of that child. The Court has wide powers to order a parent to pay child maintenance at any stage during matrimonial proceedings (such as before a divorce), or during or after the grant of divorce, judicial separation, or nullity of marriage.
Spousal Maintenance
A wife has the right to apply for wife’s maintenance before marriage or in divorce proceedings, which will only be payable until she remarries. Factors that affect the amount would be:
- Duration of the marriage
- Financial status of both the wife and the husband
- Standard of living enjoyed by both during the marriage
- Ages of the parties
Traditionally, the law in Singapore only required husband’s to pay the wife’s/ex-wife’s maintenance. This was changed in 2016, allowing a husband/ex-husband, to apply for maintenance as well if he is incapacitated by a physical or mental disability before or during the course of marriage, unable to earn a living as a result of the disability, and hence unable to support himself.
Similar to child maintenance, the Court has the power to order a husband to pay maintenance to his former wife, or order a woman to pay maintenance to her incapacitated former husband during any matrimonial proceedings. The Court has the discretion in ordering spousal maintenance to be paid either in a lump sum, or in periodic payments depending on the circumstances.
Typically, a lump sum payment is preferred as it upholds the clean break principle if the paying spouse can afford to, or if the division of matrimonial assets allows for. Monthly payment is often ordered as a matter of practicality.
Matrimonial Assets Distribution
In our experience, this aspect is the most hotly contested part of most divorces, next to children’s issues. Many inquiries actually begin with this instead of what to rely on to prove the irretrievable breakdown of marriage.
As with maintenance orders, the Court has the power to make orders for the division of matrimonial assets when granting, or after the grant of a judgment of divorce, judicial separation, or nullity of marriage, as the Court thinks is fair.
Matrimonial assets are any assets defined under the law as:
- Any assets acquired before the marriage by one party or both parties to the marriage
- Ordinarily used or enjoyed by both parties or one or more of their children while the parties are residing together for shelter/transportation or for household, education, recreational, social or aesthetic purposes
- Substantially improved during the marriage by the other party or by both parties to the marriage
- Any other asset of any nature acquired during the marriage by one or both parties to the marriage, but does not include any asset that has been acquired by one party at any time by gift or inheritance that has not been substantially improved during the marriage
This means that assets like a business or HDB flat that one spouse owned before marriage could be a matrimonial asset if the other spouse contributed to it, or was enjoyed by both and their children during the marriage. Other assets commonly deemed as matrimonial assets are the matrimonial home, CPF funds, bank account money, shares, insurance policies, investments, and businesses.
The Court will consider several factors in making an order for the division of matrimonial assets, including:
- Contributions made by each party in money, property, or work towards acquiring, improving, or maintaining the matrimonial assets
- Any debt owing by any party for their joint benefit, or the benefit of any child of marriage
- The needs of the children
- Contributions made by each party to the family, including indirect contributions and financial/non-financial contributions
- Prenuptial or postnuptial agreements entered into between the spouses
Legal Costs of Divorce Proceedings
The costs of divorce proceedings can be handled in several ways. They may be borne entirely by one party, shared between both parties, or each party may be responsible for their own costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What if my spouse is hiding assets?
For the court process to work, parties have a legal duty to the Court to provide full and frank disclosure of all assets that they have. If a party has evidence that the spouse has not made full disclosure, they may seek the help of the Court to ask questions about the hidden assets and ask for evidence to be produced in Court regarding those assets through discovery and interrogatories.
For example, in a case where a husband hid $4 million worth of assets, the wife was able to produce evidence of bank statements to prove it. Thus, the Court decided that the wife should be entitled to a proportion of those hidden assets, and also ordered the husband to receive a lower proportion of the known assets.
Divorce Process in Singapore
Broadly speaking, there are two stages to the divorce process, which we break down to (i) Divorce Application to Interim Judgment, and (ii) Ancillary Matters to Final Judgment.
Stage 1: Divorce Application to Interim Judgment
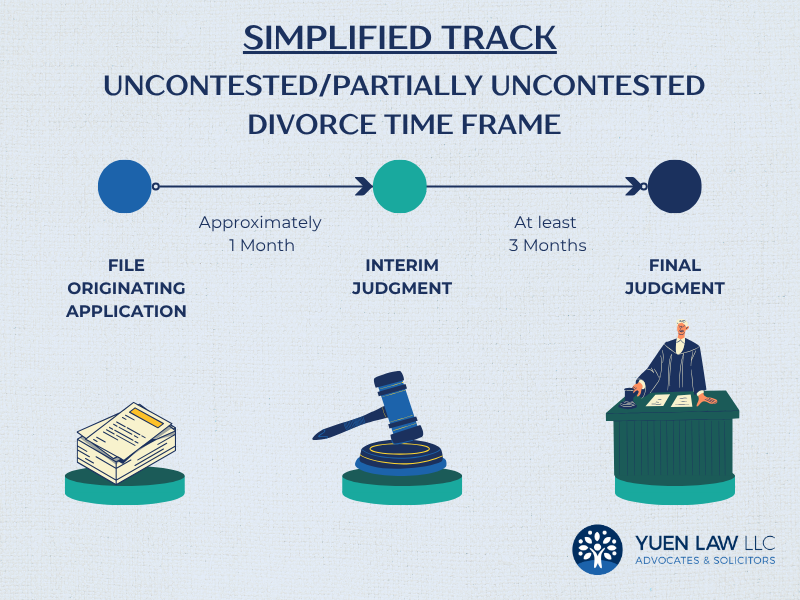
Simplified Track (Uncontested/Partially Uncontested)
Parties may proceed with the simplified track as long as they have agreed on the grounds for divorce, even if they have not reached full agreement on ancillary matters.
Originating Application (OA) for Divorce
The applicant files the Originating Application, which sets out key details such as the particulars of the applicant, respondent and children, marriage certificate, and jurisdictional basis. It also includes the specific facts relied to demonstrate that the marriage has irretrievably broken down. The applicant must also state the reliefs sought in relation to ancillary matters such as maintenance, custody, and division of assets. A bankruptcy search for both parties should be submitted together with the application.
The applicant must serve the simplified originating application on the respondent within 14 days.
Certificate of Completion from Both Parties
Where the parties have children below 21 years of age, attendance at the Mandatory Co-Parenting Programme conducted by the Ministry of Social and Family Development (MSF) is a prerequisite to commencing divorce proceedings. A Certificate of Completion will be issued upon completion of the programme, and this must be filed together with the OA.
Respondent’s Consent to Simplified Proceedings
Where the respondent is agreeable to proceeding on a simplified and uncontested basis, he or she must sign the Consent to Originating Application for Divorce confirming agreement to the dissolution of the marriage based on the grounds set out in the OA (e.g., mutual agreement, unreasonable behaviour). The respondent may also consent to draft ancillary reliefs orders, if any.
Applicant’s Affidavit of Evidence-in-Chief (AEIC)
The Applicant’s Affidavit of Evidence in Chief is a sworn statement that sets out the key facts of the marriage and the parties’ agreement to the divorce. It is the applicant’s main evidence in a simplified divorce.
The AEIC replaces the need for oral testimony. The Court will rely on it to decide whether there are valid grounds for divorce and whether the agreed terms are fair and reasonable. The AEIC must be signed before a Commissioner for Oaths and includes the applicant’s request for a hearing date.
Draft Ancillary Reliefs Orders
If the parties have reached agreement on some of the ancillary matters, the applicant must set out the agreed terms in the Draft Ancillary Reliefs Order. This includes issues such as custody, care and control of the children, access arrangements, division of matrimonial assets, and maintenance for the wife, an incapacitated husband, or the children.
If there are ancillary matters that are not yet agreed upon, the applicant should also state his claims in the simplified Originating Application.
Affidavit of Split Care and Control
In cases where each parent cares for different children, such as when the mother cares for the younger daughter, while the father has care of the older son, the Affidavit of Split Care and Control must set out the agreed living arrangements and explain why this is in the children’s best interests.
Uncontested Dissolution Hearing & Interim Judgement
After the divorce application is filed, the Court will fix a date for the Uncontested Dissolution Hearing within four to six weeks. If the Court is satisfied that the marriage has irretrievably broken down, it will grant Interim Judgment (IJ) to dissolve the marriage if it.
If both parties have reached full agreement on all ancillary matters, the Court may record the agreed terms as a Draft Consent Order at the same time.
If there is no full agreement, the unresolved ancillary matters will be dealt with at the next stage, either through mediation or at an Ancillary Matters Hearing.
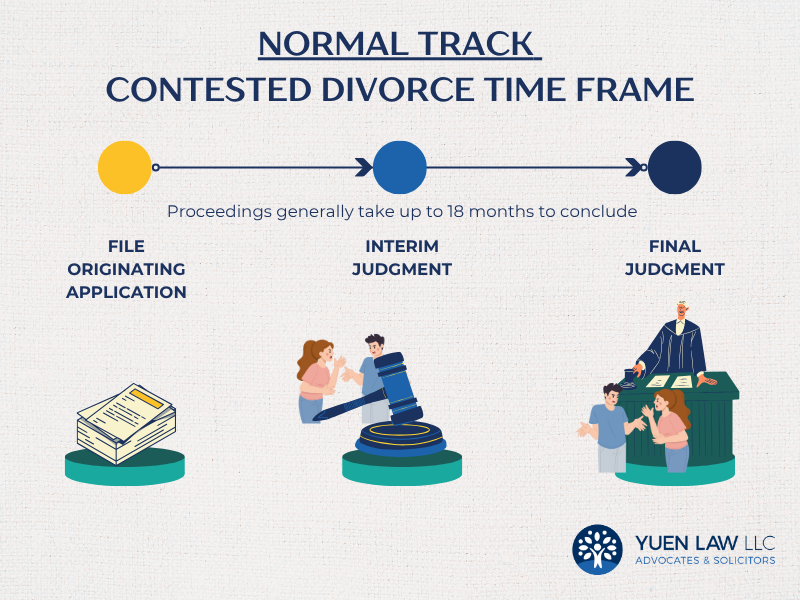
Normal Track (Contested)
In contested divorce cases, once the applicant has filed the OA and Certificate of Application, the following documents must be filed:
Notice to Contest (NTC)
If the respondent does not agree to the divorce or the proposed ancillary matters, they must file a NTC within 14 days after receiving the divorce papers.
Reply (or Cross Application and Reply)
If the Respondent wishes to contest the divorce application he or she must file a Reply within 28 days after receiving the divorce papers.
If the respondent wishes to end the marriage but on different grounds, the respondent must file a cross application together with his or her reply.
Reply to the Cross Application
If a Cross Application is filed, the Applicant must file a Reply to it within 28 days of receiving the Cross Application.
Case Conference
Once all pleadings are filed, the Court will schedule a Case Conference to manage the case and determine the next steps. The Court may also direct the parties to attend counselling or mediation, especially if there are children involved, in an effort to resolve the dispute amicably.
Affidavit of Evidence-in-Chief (AEIC)
In contested divorce, both parties are required to file their AEICs before the trial. These sworn statements set out each party’s account of the facts and the evidence they intend to rely on. The AEICs are exchanged between the parties and form the basis of their testimony during the hearing. Once the AEICs are filed and exchanged, the applicant files a request for trial date.
Contested Hearing & Interim Judgement
At a contested divorce hearing, both parties and their witnesses must attend court to be cross-examined on the contents of their Affidavits of Evidence-in-Chief (AEICs). The judge will review the evidence and decide whether the marriage has irretrievably broken down, and whether an Interim Judgment should be granted.
If the Interim Judgment is granted, the Court will schedule further case conferences to address the ancillary matters that remain unresolved. The case will then proceed to the second stage of the divorce process, where the Court will decide on issues such as custody, division of assets, and maintenance.
Stage 2: Ancillary Matters to Final Judgment
Simplified Track (Uncontested)
Final Judgment
Parties must wait three months after the Interim Judgment before extracting the Final Judgment, to formally conclude the divorce.
Normal Track (Contested)
If the parties are unable to settle the ancillary matters after private negotiations or court mediation, they are required to proceed to the second stage of the divorce procedure for the court to make orders concerning all ancillary matters.
Ancillary matters include children’s matters (including custody, care and control, access, maintenance), spousal maintenance, and division of matrimonial assets.
Ancillary Affidavits and Binding Summary of Positions
Parties are required to file and exchange their Affidavit of Assets and Means (AOM) within 28 days of the Interim Judgment. If the Court refers the matter to mediation, the filing and exchange of the first AOM will take place according to the Court’s directions.
Each party is allowed to file two rounds of AOMs as of right. If a party wishes to file a third AOM, they must first obtain the Court’s permission and provide reasons to justify the additional filing.
Documents to be included in Affidavit of Asset and Means
- Payslips or similar documents to show evidence of your income for the past 6 months.
- Your current employment contract OR similar evidence showing the current terms of your employment.
- Tax assessment notices or similar documents for the past 3 years.
- Updated ACRA search results or similar documents to show ownership of your businesses.
- Current tenancy agreement or similar evidence showing the rental you receive.
- Updated search results on your bankruptcy status from the Ministry of Law’s Insolvency Office.
- Documents to prove your monthly expenses.
- Documents to prove the child(ren)’s monthly expenses.
- Evidence that you have supported your dependents.
- Current maintenance order(s).
- Your medical report OR evidence of your incapacity to work.
- Updated mortgage statement showing the outstanding mortgage loan.
- Updated valuation report or transaction history to show the value of the property.
- Updated bank account statements for the past 3 months.
- Updated CPF statement showing the balance in each account.
- Updated CPF investment account statements from the banks / investment companies.
- Updated statement showing the balance in the pension funds (excluding CPF).
- Terms and conditions of the pension scheme OR similar evidence to show how the scheme works (excluding CPF).
- Updated Central Depository Pte Ltd statements OR similar evidence to show the balance and details of your investments.
- Updated ACRA search results OR similar evidence to show your shareholdings.
- Evidence of the value of your investments or shares.
- Insurance policy documents OR similar evidence to show the surrender values and beneficiaries of your insurance policies.
- Evidence of your insurance premiums and the payment mode.
- Evidence of vehicle ownership.
- Updated hire purchase statement.
- For other valuables (antiques, artwork, fine jewellery, fine wine, branded goods, club memberships etc.) in Singapore or overseas: valuation report OR similar documents to show value of items.
- Evidence of the debts owed to you.
- Updated statements OR similar documents to show the outstanding balance of the debt.
- Evidence to show why the debt was incurred.
- Evidence to show why some assets are not matrimonial assets.
- Updated CPF housing withdrawal statement OR similar evidence to show use of CPF monies for the assets.
- Evidence of other payments made for the purchase of the assets.
If one spouse needs additional documents from the other spouse to address ancillary matters, they can file and serve a Summons for Disclosure.
After Ancillary Affidavits are filed, the Court will require parties to file a binding summary setting out a summary of parties respective position in respect of the outstanding ancillary issues.
Contested Ancillary Matters Hearing & Final Judgment
The Court will schedule a hearing for the ancillary matters, during which the parties or their lawyers will present both written and oral submissions. The Court will then make a decision on the outstanding issues, and make appropriate orders to finalise the divorce.
This Final Judgement Order is legally binding, and both parties are expected to comply with it. For example, they may be required to sell their HDB flat or pay maintenance as ordered.
Divorce Rate in Singapore (Updated 2024)

The divorce rate in Singapore has remained largely stable at about 7,000 a year, with a low of 6,959 in 2020 and peaking at 7,890 in 2021.
The average duration of civil marriage increased to 12.0 years in 2024, up from 10.5 years in 2014 and 9.9 years in 2004.

According to the Singapore Department of Statistics, the majority of divorces in 2024 were filed by women. The top reason for divorce cited by both women and men was “unreasonable behaviour,” accounting for 62.6% of cases for women and 48.5% of cases for men in 2024.
Marriages in their 5th to 10th anniversary had the highest rate of divorce, and highest in remarriages by divorcees. The second highest rate of divorce occurred where one partner was a divorcee. Couples who had married for the first time had the lowest dissolution rates. Divorce rates were also highest in couples whose educational levels were “secondary” and below, and lowest in couples with university qualifications.
Strategic Divorce Solutions with Expert Guidance
At Yuen Law, our team of divorce lawyers, led by Lim Fung Peen, head of our Private Wealth and Family Practice with over 25 years of experience, provides strategic solutions for divorces and post-divorce matters, including flat ownership transfers, sales, and will updates. We are dedicated to guiding our clients through this emotional journey with expert advice and tailored strategies to achieve the best possible outcomes for them.






